Foreword
In 1978, China started the historic process of reform and opening-up. This is a glorious chapter in the development epic of the country and the nation composed by the Chinese people, recording the great journey of common progress of China and the rest of the world. It has not only profoundly changed the country, but also greatly influenced the whole world. Over the past 40 years, China has been adhering to the fundamental national policy of reform and opening-up and pursuing development with its door wide open. A model of all-round, multi-level, and wide-ranging opening-up has gradually taken shape. China is closely connected with
the outside world and has made a significant contribution to the noble cause of global peace and development.
In 2001, China acceded to the World Trade Organization (WTO). This was a milestone in China’s integration into economic globalization, marking a new historic stage of reform and opening-up. Since its accession to the WTO, China has been a strong advocate for free trade. China has comprehensively fulfilled its commitments to the WTO, substantially opened its market to the world, and delivered mutually beneficial and win-win outcomes on a wider scale. Through these efforts, China has lived up to its responsibility as a major country.
The multilateral trading system, with the WTO at its core, is the cornerstone of international trade and underpins the sound and orderly development of global trade. China firmly observes and upholds the WTO rules, and supports the multilateral trading system that is open, transparent, inclusive and non-discriminatory. China has participated in all aspects of WTO work, made its voice heard and contributed its own proposals on improving global economic governance. China is an active participant, strong supporter and major contributor in the multilateral trading system.
Accession to the WTO has boosted China’s development and benefited the rest of the world. Propelled by a new vision of development, the Chinese economy is transitioning from rapid growth to high-quality development. China has become a major stabilizer and driving force for the world economy. China stays committed to the strategy of opening-up for win-win results, vigorously promotes the Belt and Road Initiative, and shares opportunities and benefits with other countries and their people while developing China itself, enhancing global wellbeing and common prosperity.
At the historic starting point of a new era, China’s door of opening-up will not be closed and will only open even wider. Opening-up was key to China’s economic growth over the past 40 years. In the same vein, high-quality development of China’s economy in the future can only be achieved with greater openness. China will continue adhering to the fundamental national policy of reform and opening-up. China will more proactively embrace economic globalization, adopt policies to promote high-standard liberalization and facilitation of trade and investment, and work together with other countries to build a community of shared future with extensive converging interests and a high degree of interdependence.
The Chinese government is publishing this white paper to give a full account of China’s fulfillment of its WTO commitments, to explain China’s principles, stances, policies, and propositions regarding the multilateral trading system, and to describe China’s vision and actions in advancing higher-level reform and opening-up.
I. China Has Faithfully Fulfilled Its WTO
Accession Commitments
Since China acceded to the World Trade Organization[1] in 2001, it has made continued efforts to improve its socialist market economy system, further align its policies with multilateral trade rules in all areas, honor its commitments on opening trade in goods and services, and strengthen intellectual property rights (IPR) protection. Remarkable improvements have been made in enhancing the stability, transparency, and predictability of its opening-up policies. China has contributed significantly to the effective operation of the multilateral trading system.
1. Improving the socialist market economy and relevant legal system
Consistently reforming to develop the socialist market economy. China has accelerated efforts to improve the socialist market economy system and strengthen the market system. This has involved reorganizing the relationship between the government and the market, letting the market play the decisive role in resource allocation and the government play its role better. Education campaigns on WTO rules have been extensively rolled out, raising public awareness of the market, competition, rules and the concept of rule of law.
Continuously improving the legal system of socialist market economy. Upholding the rule of law, China has faithfully observed and implemented WTO rules, improved its laws and regulations on market economy, and built up a legal system in line with multilateral trade rules. After its accession, China launched major efforts to review and revise relevant laws and regulations, involving 2,300 laws, regulations and departmental rules at central government level, and 190,000 policies and regulations at sub-central government levels, covering trade, investment, IPR protection, etc. In 2014, China issued an official document on furthering trade policy compliance with WTO rules, requiring government at all levels to assess proposed trade policies in accordance with WTO agreements and China’s commitments. In 2016, China set up a legality review mechanism to examine normative documents, enhancing the transparency of and public participation in policy development.
2. Fulfilling commitments on trade in goods
Substantively reducing import tariffs. By reducing import costs to boost trade, China has shared its development dividend and growing markets with the rest of the world. By 2010, China had fulfilled all of its tariff reduction commitments, reducing the average tariff level from 15.3 percent in 2001 to 9.8 percent. It lowered the average tariff rate of manufactured goods from 14.8 to 8.9 percent. It cut the average tariff rate of agricultural products from 23.2 to 15.2 percent, about one fourth of the global average and far lower than those imposed by the WTO’s developing members (56 percent) and developed members (39 percent). China’s maximum bound tariff rate of agricultural products is 65 percent, while the corresponding rates of the United States, the European Union and Japan are 440, 408 and 1,706 percent respectively.
Significantly lowering non-tariff barriers. To increase transparency and facilitate trade, China has reduced unnecessary trade restrictions. By January 2005, in accordance with its commitments, China had eliminated import quotas, import licenses, specific import tendering requirements and other non-tariff measures with regard to 424 items such as automobiles, machinery and electronics products, and natural rubber. It introduced tariff rate quota administration for important bulk commodities, i.e. wheat, corn, rice, sugar, cotton, wool, wool top, and chemical fertilizers.
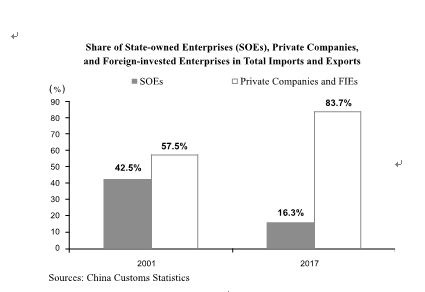
Liberalizing the right to trade. To diversify entities and stimulate their enthusiasm to engage in foreign trade, in July 2004 China replaced approval system with registration system for foreign trade authorization, releasing immense vigor of private businesses which has led to a surge of foreign trade in the private sector. With rapid growth and an increasing share of the market, private companies have become important actors in China’s foreign trade. In 2017, foreign trade by private companies and foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) accounted for 83.7 percent of the country’s total trade volume, up from 57.5 percent in 2001. In 2017, Chinese private companies, which take the largest share of China's exports, contributed 46.6 percent of all goods and services exported.
3. Fulfilling commitments on trade in services
Extensively opening up the services market. China has striven to boost the services industry and increase its share of contribution to the economy. Of the 160 services sub-sectors under the 12-sector WTO classification, China committed to opening up 100 sub-sectors under 9 sectors, a level approximate to the average 108 sub-sectors committed by the developed members of the WTO. By 2007, China had honored all of its commitments on trade in services.
Continuously reducing restrictions. China has step by step lowered the threshold for foreign investment to enter the services sectors in China, lifted geographical and quantitative restrictions on services according to schedule, and constantly broadened the business scope for foreign investment in the services sectors. China has permitted wholly foreign-owned enterprises in 54 sub-sectors such as courier, banking and property insurance services, allowed foreign majority ownership in 23 sub-sectors such as computer and environment services, and accorded national treatment to foreign capital in 80 sub-sectors such as telecommunication, rail transport, and tourism services. In 2010, foreign direct investment (FDI) flowing into China’s services industry surpassed that into manufacturing industry for the first time. In 2017, FDI in the services industry made up 73 percent of all FDI in China.
4. Fulfilling commitments on IPR protection
Strengthening IPR protection on China’s own initiative. Strengthening IPR protection is the centerpiece for improving the property rights protection system, and it would provide the biggest boost to the competitiveness of the Chinese economy. It not only serves China’s own development needs, but also helps cultivate a business environment that is law-based, internationalized and business-friendly. China encourages technological exchanges and cooperation between Chinese and foreign enterprises, and protects the lawful IPR owned by foreign enterprises in China. At the same time, we hope foreign governments will also improve protection of Chinese IPR.
Building a full-fledged legal system on IPR protection. Since acceding to the WTO, China has formulated and improved its laws and regulations on IPR protection, set up IPR working mechanisms with many countries, drawn upon advanced international legislative practices, and built an IPR legal system that conforms to WTO rules and suits national conditions of China. The amended Trademark Law sets up a system of punitive damages. The amended Anti-Unfair Competition Law improves the protection of trade secrets, identifies act of confusion, introduces the concept of sign and expands the scope of protection for sign. Currently China is working on amending the Patent Law and the Copyright Law.
Continuously strengthening law enforcement on IPR protection. China has enhanced the dominant role of the judiciary in IPR protection to significantly raise the cost for offenders and fully unlock the deterrent effect of relevant laws. The State Intellectual Property Office has been restructured to strengthen law enforcement. China has set up three IPR courts in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou, and special judicial organs at 15 intermediate courts in Nanjing, Suzhou, Wuhan, Xi’an and other cities to handle cross-regional IPR cases, including those related to patents. China strengthened administrative law enforcement on intellectual property protection and launched special campaigns targeting outstanding problems, which effectively protected intellectual property rights. Such campaigns include “Convoy Campaign” for protecting patent rights, the “Sword-net Campaign” for combating online infringement and piracy, the “Sweeping Campaign” for cracking down pornography and illegal publication in the copyright field, the “Network Sword Campaign” for combating IPR infringements and counterfeits and the “Sword Actions on Quality Control” for cracking down counterfeits.
Attaining notable results in IPR protection. Since 2001, intellectual property royalties paid by China to foreign right holders has registered an annual growth of 17 percent, reaching USD28.6 billion in 2017. In 2017, China received 1.382 million invention patent applications, ranking the first in the world for the seventh consecutive year. Nearly 10 percent of the applicants were foreign entities and individuals. Invention patent applications filed by foreign entities and individuals in China reached 136,000, growing by threefold compared with 33,000 in 2001. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, 51,000 patent applications filed from China through the Patent Cooperation Treaty were accepted in 2017, second only to the US.
5. Fulfilling commitments on transparency
Providing a solid legal basis. The Legislation Law, the Regulations on Procedures for Formulation of Administrative Regulations, and the Regulations on Procedures for Formulation of Rules explicitly provide for the solicitation of public comments on draft laws, administrative regulations and rules. The legislative affairs commission of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress regularly publishes the Laws of the People’s Republic of China (English edition); the State Council’s legislative affairs organ regularly publishes the Laws and Regulations of the People’s Republic of China Governing Foreign-Related Matters (Chinese and English bilingual edition); and the Ministry of Commerce regularly publishes trade policies in China Foreign Trade and Economic Cooperation Gazette.
Comprehensively implementing the WTO notification obligations. China has submitted notifications to the WTO on a regular basis concerning the amendment, revision and implementation of relevant laws, regulations and measures as required by the WTO. By January 2018, China had submitted over one thousand notifications covering areas such as central and sub-central subsidy policies, agriculture, technical regulations, standards, conformity assessment procedures, state trading, trade in services, and IPR laws and regulations.
6. Making tremendous efforts to honor its commitments
China made extensive and profound commitments on opening up when entering the WTO. Domestic companies were confronted with international competition, and most industries faced great difficulties. Rising up to these challenges, Chinese companies took the initiative to promote structural readjustment, participated in the global value chains and significantly increased their international competitiveness.
Box 1. The Automobile Industry’s Costly Adjustment |
Before WTO accession, China’s automobile industry lagged far behind developed members in terms of production scale, product quality, manufacturing technology, R&D capacity, costs and prices, and brand development. After accession, China faithfully fulfilled its commitments to slash customs duties on automobiles. By July 1, 2006 when the transitional period ended, China had lowered the duties on imported automobiles from 100 to 25 percent. China’s auto industry was hit hard by cheaper imported cars and mounting competition. For example, China imported USD37.91 billion worth of passenger cars with engine displacement at 1.5-3L in 2017, compared to USD890 million in 2001. This represented an annual growth of 26.4 percent, with the auto trade deficit surging from USD870 million to USD34.35 billion. Facing the pressure, China’s auto industry took the initiative to carry out large-scale restructuring, opened wider to foreign capital, raised its levels of technology, management and services amidst fierce competition, and steadily penetrated the global value chains. |
II. China Firmly Supports the Multilateral Trading System
The multilateral trading system with the WTO at its core is the cornerstone of international trade, and has been playing a pivotal role in promoting global trade and building an open world economy. Since its accession to the WTO, China has firmly supported the multilateral trading system, participated in all aspects of WTO work. It called upon the WTO to focus more on the concerns of developing members, opposed unilateralism and protectionism, upheld the authority and efficacy of the multilateral trading system, and made concerted efforts with other members in supporting the WTO to play a greater role in economic globalization.
1. Liberalizing and facilitating trade and investment
Participating fully in the Doha Round negotiations. China has submitted or co-sponsored more than 100 negotiation proposals, helped secure agreement on trade facilitation and export competition in agricultural products, and promoted the continuous improvement of the multilateral trading system. In 2015, China became the 16th WTO member to ratify the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA). During its G20 presidency in 2016, China encouraged a number of countries to complete their domestic ratification procedures of the TFA, prompting the agreement’s entry into effect at an early date.
Promoting plurilateral trade liberalization. As a developing country, China has actively participated in plurilateral liberalization initiatives and made important contributions to relevant talks. It accepted the Information Technology Agreement (ITA) upon accession, subsequently participated in the negotiations to expand its coverage, and encouraged relevant parties to reach agreement on eliminating tariffs of 201 information technology products. As one of the initiators of the negotiations on the Environment Goods Agreement, China always participated in relevant discussions in a constructive manner, and contributed to the important consensus reached at the G20 Summit in Hangzhou. In 2007, China started the negotiation on its accession to the Agreement on Government Procurement and has been making great efforts ever since.
Mobilizing support for discussing new issues in the WTO. China has encouraged the WTO to respond to and discuss new topics of general interest to the members such as investment facilitation, micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), and e-commerce. China initiated “Friends of Investment Facilitation for Development (FIFD)” and sponsored the Joint Ministerial Statement on Investment Facilitation for Development signed by over 70 members. China joined the “Friends of Micro, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises”, and shared with other members its proposals that support MSMEs. As an advocate of multilateral discussions on e-commerce in the WTO, China joined “Friends of E-commerce for Development (FED)”, shared its experiences and helped other developing members benefit from e-commerce.
Faithfully implementing the Trade Facilitation Agreement. As a developing member, China has actively promoted the implementation of TFA. It has set up the National Committee on Trade Facilitation to coordinate the efforts of relevant government agencies to enhance trade facilitation. By 2017, China’s provinces (as well as autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) had all established a joint committee mechanism for trade facilitation in their respective jurisdictions. Regarding China’s TFA commitments, 94.5 percent of all commitments fall into Category A (immediately implemented upon entry into force of the TFA), and only four items belong to Category B (implemented after a transitional period following the TFA’s entry into force). China will honor its promise and implement all the Category B measures following a transitional period of three years after entry into force of the Agreement.
2. Safeguarding the dispute settlement mechanism
Safeguarding the effective operation of the dispute settlement mechanism. The WTO dispute settlement mechanism has played a vital role in maintaining the predictability of international trade and the stability of the multilateral trading system. China has actively participated in the negotiations on improving the Understanding on Rules and Procedures Governing the Settlement of Disputes and supports the independence and impartiality of the WTO Appellate Body. Despite the attempt of certain WTO member to obstruct the appointment of members of the Appellate Body, China joined more than 60 members in submitting a proposal on starting the selection process at the earliest possible date.
Properly handling trade disputes with other WTO members. China supports WTO members to solve their trade disputes within the WTO dispute settlement mechanism. By April 2018, China had brought 17 disputes to the WTO, of which 8 had been concluded. Meanwhile, China had been complained against in 27 disputes, of which 23 had been concluded. By lodging complaints in the WTO, China redressed other members’ violation of obligations under the covered agreements, and defended its own trade interests as well as the authority of WTO rules. China also actively defended the cases against it, respected the WTO rulings, and made adjustments to its measures according to WTO rules. Up to now, none of the complainants has requested for retaliation against China.
3. Fully participating in trade policy review
Attaching great importance to trade policy monitoring by other WTO members. The WTO trade policy review (TPR) mechanism is effective in enhancing the transparency of the multilateral trading system. China places great emphasis on the TPR process. Having undergone six TPRs on itself, China is preparing for the seventh one in July 2018. In an open and frank manner, China has briefed the WTO membership on its macro-economic, trade and investment policies, and listened attentively to their comments and suggestions on China’s reform and opening-up. Other WTO members applaud China’s active participation and regard China as an impressive example in reinforcing the role of TPR in monitoring commitments, ensuring compliance and enhancing openness.
Urging other WTO members to abide by multilateral trade agreements. Since its accession to the WTO, China has participated in nearly 300 TPRs on other members. It raised thousands of written questions and trade concerns to the members under review, urged them to abide by the WTO rules and their commitments, and played a positive role in safeguarding and strengthening the TPR mechanism.
Supporting the WTO to focus on development. An important objective of the WTO is to ensure that developing members, especially least-developed country members, benefit from international trade and boost their economic growth. As the largest developing country, China understands the difficulties of developing members to benefit from the global value chains and participate in international economic and trade governance. China worked hard to make trade an enabler of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Providing pragmatic and effective support to other developing members. China has reinforced its aid to other developing members, especially least-developed country members, to bridge the South-North development gap. By March 2018, it had accorded zero tariff treatment on 97 percent of all tariff lines to 36 least-developed countries (LDCs) that have diplomatic relations with China and completed exchange of notes. Responding to the “Aid for Trade” initiative, China has contributed multilateral and bilateral resources to help other developing members, especially least-developed country members, with infrastructure construction, professionals training, productivity improvement, as well as trade and investment development. It has donated USD1 million to the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement Facility to assist the implementation of the TFA. The LDCs and Accessions Program, established by China in 2011, has helped six LDCs accede to the WTO. Since 2017, China has strengthened cooperation with the WTO and other international organizations under the South-South Cooperation Assistance Fund, and carried out cooperative projects in “Aid for Trade” to help other developing members benefit from global value chains.
5. Firmly opposing unilateralism and protectionism
Unilateralism and protectionism run counter to the fundamental principles of the WTO. The multilateral trading system is a historic choice that follows the trend of global economic development. The WTO advocates the principles of rules, openness, transparency, inclusiveness and non-discrimination, and it will remain the main channel to address global trade issues. China explicitly opposes unilateralism and protectionism. Unilateralism goes against the law of the market and international rules, causes injury to others but ends up defeating oneself. Pursuing protectionism is like locking oneself in a dark room. While wind and rain may be kept outside, that dark room will also block light and air. Only through equal consultation and joint efforts can win-win results be achieved for all.
Pursuing free trade through platforms for multilateral cooperation. China advocates solving international trade problems through cooperation, dialogue and consultation on an equal footing. During the 22nd APEC Economic Leaders’ Meeting, the G20 Hangzhou Summit, and the BRICS Xiamen Summit, all hosted by China, the country increased coordination with all parties concerned, and secured statements on opposing trade protectionism in the outcome documents of these summits. When attending the Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation, the Boao Forum for Asia, and the World Economic Forum, Chinese leaders repeatedly expressed their firm support for the multilateral trading system and an open world economy. In the WTO, the vast majority of members echoed China’s opposition to unilateralism and protectionism.
III. China’s Significant Contribution to
the World After Accession to the WTO
China steadfastly pursues a mutually beneficial opening-up strategy, upholds the WTO’s principle of free trade, and has lived up to its responsibilities as a major country in the process of opening-up. From its WTO accession in 2001 to the Belt and Road Initiative in 2013, China has embraced the world with open arms, made a significant contribution to promoting international trade and increasing global wellbeing, and become a key anchor and driver for the world economy.
1. Boosting world economic recovery and growth
Since its accession to the WTO, China has accelerated its reform and opening-up process and economic growth. China’s development is a forceful driver of global economic growth.
In 2016, China’s GDP accounted for 14.8 percent of the world total, up by 10.7 percentage points over 2001, calculated at exchange rates. Since 2002, China’s contribution to global economic growth has approached 30 percent on average. The Chinese economy has become a major engine for global economic recovery and growth.
China has quickened its pace in promoting new industrialization, IT application, urbanization, and agricultural modernization, created enormous opportunities for consumption and investment, and generated more jobs for the world. According to a report released by the International Labor Organization, “Effects of China on the Quantity and Quality of Jobs in Latin America and the Caribbean”, China created 1.8 million jobs for Latin America and the Caribbean region from 1990 to 2016.
China’s rapid development has made tremendous contributions to the cause of global poverty reduction. Over the past 40 years of reform and opening-up, the Chinese people have emerged from scarcity to abundance and from poverty to moderate prosperity. According to current UN standards, more than 700 million Chinese people have been lifted out of poverty, accounting for more than 70% of the global total over the same period. This represents the largest contribution to poverty reduction in the world.
2. Foreign trade development benefiting the world
Since China’s entry into the WTO, China’s foreign trade has maintained sustained development, benefiting more than 1.3 billion Chinese and other peoples across the world.
Confronted with unprecedented difficulties and challenges including the global financial crisis in 2008, China has taken effective measures to stabilize and revitalize its foreign trade. According to WTO statistics, China’s imports accounted for 10.2 percent of the world total merchandise import in 2017, and its exports 12.8 percent, making China a major trade partner of more than 120 countries and regions. China’s exports have provided high-quality and inexpensive products to businesses and people around the world. From 2001 to 2017, China’s imports increased by an annual average of 13.5 percent, 6.9 percentage points higher than the global average; and China has become the world’s second largest importer. Since 2009, China has been the largest export market for the LDCs, and absorbed 20 percent of their exports.
China’s services imports increased from USD39.3 billion in 2001 to USD467.6 billion in 2017, up by an annual average of 16.7 percent, and accounting for nearly 10 percent of the world total. Since 2013, China has been the world’s second largest service importer, making significant contributions to stimulating consumption, creating jobs and boosting economic growth in the exporting countries. Taking tourism services as an example, China has been the world’s largest source of outbound tourists for many years in a row. In 2017, outbound tourist trips made by Chinese citizens exceeded 130 million person-times, generating USD115.29 billion of overseas tourism spending.
China’s innovation in trade models has also given new impetus to world trade growth. Cross-border e-commerce and other new types and modes of foreign trade have flourished in China, providing an ever-expanding market to its trading partners. In 2017, the value of imported and exported goods in cross-border e-commerce checked and released by China Customs totaled RMB90.24 billion, up by 80.6 percent on yearly basis, of which imports stood at RMB56.59 billion, up by 120 percent compared with the previous year.
3. Two-way investment benefiting all countries
China has been promoting the establishment of a fair, equitable and transparent system of international trade and investment rules to boost the orderly flow of production factors, efficient resources allocation and full market integration.
China has proactively attracted foreign institutions and individuals to invest and develop in China. Since 1992, China has consistently topped the list of FDI recipients among developing countries for 26 years consecutively. After China’s accession to the WTO, its FDI increased from USD46.88 billion in 2001 to USD136.32 billion in 2017, up by an annual average of 6.9 percent. FIEs have shared the benefits of China’s economic development, while helping improve the quality and performance of China’s economy. According to the “2018 China Business Climate Survey Report” by the American Chamber of Commerce in China (AmCham China), nearly 60 percent of the interviewed enterprises ranked China as a top three investment priority; some 74 percent of the AmCham China member enterprises plan to expand their investments in China in 2018, the highest in recent years, and one third of the interviewed enterprises plan to increase their investments in China by over 10 percent. According to the “Business Confidence Survey 2018” by the European Union Chamber of Commerce in China, more than half of its member enterprises plan to expand their presence in China. In 2017, newly founded FIEs in China reached 35,652, registering an increase of 27.8 percent.
China’s outward investment cooperation has developed in a sustained, sound, and orderly way. In terms of annual flow of outward direct investment (ODI), China’s world ranking rose from the 26th place after its accession to the WTO to the third in 2017. China’s outward investment cooperation has accelerated technological progress in the host countries, advanced their economic development, improved their people’s well-being and created many jobs.
4. Providing public goods to the world
China receives support from the international community in its own development process and stands ready to provide more public goods to the world. China is committed to building an open platform of cooperation, upholding and growing an open world economy, and working together with other countries to build a broad community of shared interests.
Proposing the Belt and Road Initiative. In the face of difficulties in world economic development, China put forward the Belt and Road Initiative in 2013. While the proposal was initiated by China, the opportunities and achievements belong to the world. The Belt and Road Initiative plays an important role in promoting in-depth cooperation and common development between countries and regions, upholding and growing an open world economy, making economic globalization open, inclusive, balanced, win-win and beneficial to all and advancing the building of a community with a shared future for mankind.
Since 2013, more than 80 countries and international organizations have signed cooperation agreements with China. The in-depth and practical cooperation between China and relevant countries has achieved fruitful results. From 2013 to 2017, the total value of China’s trade with other Belt and Road countries exceeded USD5 trillion, and total investment by Chinese enterprises in these countries exceeded USD70 billion. By the end of 2017, Chinese enterprises had set up 75 overseas economic and trade cooperation zones in relevant countries, contributed more than USD1.6 billion taxes to the host countries and created 220,000 local jobs. Within three years starting from 2018, China will provide RMB60 billion worth of aid to the developing countries and international organizations participating in the Belt and Road Initiative, with a view to developing more projects to improve people’s lives.
Hosting the China International Import Expo. Initiated by China, the China International Import Expo (CIIE) will bring together multiple international organizations and more than 100 countries. It is an international public product that promotes inclusive and mutually beneficial development around the globe. The inaugural session of CIIE will be held in November 2018. Hosting the CIIE is an important decision made by China to promote a new round of high-level opening-up, a major policy measure of China to further open its market to the world, and a concrete action by China to support economic globalization and trade liberalization. In the coming 15 years, China is expected to import USD24 trillion worth of goods. The CIIE will provide new export opportunities for the world, build a new platform for other countries and regions to share China’s development dividends, and bring more dynamism to world economic growth.
IV. China Is Actively Advancing
Opening-Up to a Higher Level
Fulfilling China’s WTO commitments has never been the end point of its opening-up. In the face of the overwhelming trend of economic globalization and its winding path, China keeps pace with the times, takes firm steps to expand opening-up, and makes continuous efforts to open up in a more comprehensive, profound and diversified way, with a view to achieving greater mutual benefit and win-win outcomes.
1. Promoting balanced development of trade
China pursues a trade strategy of mutual benefit, win-win, diversification and balanced development. It endeavors to raise the quality and added-value of its exports, proactively increase imports, and better integrate into the global value chains. China never deliberately pursues trade surplus in goods. At the same time, China takes an objective view towards existing trade deficit in services. The country always welcomes imports that diversify market supply, improve people’s quality of life, and upgrade its industrial structure. In recent years, on top of its commitments to the WTO, China has self-initiated significant reductions to import tariffs on an interim basis for multiple times. According to the WTO, China’s trade-weighted average import tariff rate had fallen to 4.4 percent in 2015, only 1.5 to 2 percentage points higher than those of developed economies such as the US and the EU. By the end of 2017, China had reduced tariffs on more than 900 tariff lines. At the 2018 Boao Forum for Asia Annual Conference, China announced plans to further reduce import tariffs and to import more high-quality, distinctive products that meet the strong demand of the Chinese people.
Box 2. China Takes Concrete Action to Expand Imports |
At the Boao Forum for Asia Annual Conference held in April 2018, China announced plans to increase imports. It has since taken effective measures to put its plans into action. From May 1, 2018, China was to eliminate import tariffs on all common drugs including cancer drugs, alkaloid-based drugs that can treat cancer, and imported traditional Chinese medicine. All imported cancer drugs are now exempted from tariffs. From July 1, 2018, China is to reduce the most-favored-nation (MFN) tariffs for automobiles from 25 percent and 20 percent to 15 percent, and for auto parts from 25 percent to 6 percent. As a result, China’s average MFN rates will have fallen to 13.8 percent for automobiles and 6 percent for auto parts. From July 1, 2018, China is to cut MFN tariffs for 1,449 consumer products from an average MFN rate of 15.7 percent to 6.9 percent, representing an average reduction of 55.9 percent. The country will further increase imports of goods and services to meet the rising needs of its consumers and to enhance the quality of its economic development. This will also boost economic growth and employment in other countries and regions. The aforementioned measures for reducing tariffs and expanding imports will provide abundant supplies to meet diverse domestic demand and promote China’s supply-side structural reform and industrial restructuring and upgrading. |
2. Facilitating international trade
China’s efforts to implement the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement, which entered into force in February 2017, have resulted in impressive improvement in China’s trade facilitation. The average time for customs clearance has been reduced to less than 20 hours for imports and less than two hours for exports. China has accelerated the establishment of a single window for international trade. By the end of 2017, the China International Trade Single Window had been connected to 11 authorities and agencies responsible for border control and covered basically all major import and export procedures. This one-stop system enables traders to use a single entry point to declare freight and taxes with a single submission of documents, and track the results after a single joint inspection by the participating authorities. It has accelerated the modernization of China’s port management. China will further optimize supervision and management approaches, reform port administration regime and streamline procedures and reduce costs for import and export, to create a more business-friendly environment at the port.
3. Substantially widening market access for foreign investment
China has adopted a foreign investment administration model of pre-establishment national treatment plus negative list. This move marks an institutional reform in response to new developments in economic globalization and changes in international rules for investment. In September 2016, the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress amended four laws including the Law on Foreign Invested Enterprises. For those foreign-invested enterprises not subject to the special administrative measures on access to foreign investment (the negative list), their establishment and changes are now administered by a “filing for record” approach instead of the examination and approval system. In the first half of 2018, revision of the negative list for foreign investment was completed and the “Notice of the State Council on Measures for Using Foreign Investment Actively and Effectively to Promote High-Quality Economic Development” was issued to further widen market access considerably. China is making efforts to steadily liberalize its financial sector, constantly open up the services industry, and deepen the opening-up of agricultural, mining and manufacturing sectors.
As regards the shipbuilding industry, China will lift foreign equity caps for companies engaged in the design, manufacturing and repair of vessels in 2018. Moreover, China will lift foreign equity caps on airplane manufacturing of trunk airliners, regional jets, utility aircrafts, helicopters, drones and lighter-than-air aircrafts. In the automobile industry, China will remove foreign equity caps on manufacturing of special-purpose vehicles and new-energy vehicles, and phase out those on all automotive ventures over the next five years.
Box 3. China Further Opens up Its Financial Sector to Foreign Investment |
Since its accession to the WTO, China has advanced reform of its financial system and pushed the opening of its financial market into further depth and width. From the end of 2017, China has announced a series of new measures to open up its financial sector, to lower the threshold for market access and expand the business scope of foreign investors, including: • Lifting market access restrictions on bank card clearing institutions and non-bank capayment institutions, easing restrictions on credit rating services by foreign financial services companies, and granting national treatment to foreign credit information service suppliers; • Removing foreign equity caps on banks and financial asset management companies, and allowing foreign banks to set up both branches and subsidiaries in China; • Canceling the requirement that foreign insurers must have a representative office in China for two years before they can establish commercial presence, allowing eligible overseas investors to engage in insurance agency and insurance assessment businesses, and lifting restrictions on the business scope of foreign invested insurance brokerage companies; • Raising foreign equity cap to 51 percent in securities, fund management, futures, and life insurance companies, and removing the limitations after three years; • Encouraging foreign investment in financial services in the banking sector, including trust, financial leasing, auto finance, currency brokerage, and consumer finance; and • Applying no cap on foreign equity for new financial asset investment companies and wealth management companies sponsored and incorporated by commercial banks. These measures will open up China’s financial sector far beyond China’s commitments under the WTO. In the future, China will take further steps to open up its financial industry and develop a more open financial system that is internationally competitive and commensurate with China’s economic scale and influence. |
4. Creating a more attractive environment for foreign investment
China makes efforts to create a favorable and orderly investment environment, ease market access for foreign investment, further simplify the administrative procedures on access to foreign investment, build pilot free-trade zones (FTZs) with high standards, and better promote and protect foreign investment. China works to improve an investment climate that conforms to international rules, facilitates foreign investment and is based on the rule of law, and to make its market more transparent and better regulated. These efforts will help attract more foreign investment into China and ensure its effective utilization.
By March 2018, all items for non-administrative license approval had been cancelled, and items for administrative approval had decreased by 44 percent as compared to March 2013. The number of investment projects by enterprises subject to verification of the central government had been reduced by 90 percent. China has comprehensively reformed its systems for business registration and registered capital, rolled out the subscribed capital registration system, and revoked 87 percent of the items subject to examination and approval preceding the industrial and commercial registration. The time for business establishment has been shortened by at least one third. In order to alleviate the burden on businesses, China is advancing the reform of the negative list for market access, promoting the concept of “everything that is not forbidden is allowed”, and reinforcing the impartiality of law enforcement.
China will continue with the reform to streamline administration, lower taxes, and reduce fees. China will further align its business environment with international economic and trade rules, enhance policy transparency, strengthen the protection of property rights, advance the rule of law, encourage competition and oppose monopoly. The enactment of the Law on Foreign Investment will be expedited to build a legal system for foreign investment that meets the needs of reform and opening-up in the new era, elevate opening-up to a higher level, push for deeper reform in the foreign investment administration system, and protect the legitimate rights and interests of foreign investment and foreign investors. The threshold will be lowered for foreign talents to work and start their own businesses in China. In addition, China will improve various development zones, build the pilot FTZs with high standard and good quality, and explore the construction of free-trade ports with Chinese characteristics.
5. Regulating outward investment
China encourages its enterprises to abide by local laws, fulfill corporate social responsibilities and observe business principles and international practices when they do business in host countries and conduct outward investment cooperation. China will continue to promote the sustainable, reasonable, orderly and sound development of outward investment, and effectively prevent risks of all kinds. Meanwhile, in order to create a more equitable, transparent and predictable environment for foreign investment, China calls on host countries to refrain from abusing security review or adopting other restrictive practices to impose excessive limitations on foreign investment.
6. Advancing the Free Trade Area Strategy
The multilateral trading system and regional trade arrangement are the two wheels driving economic globalization forward. China upholds the multilateral trading system and promotes free trade arrangements. By May 2018, China had signed 16 free trade agreements (FTA) with 24 countries and regions. In 2017, trade between China and its FTA partners (excluding Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region, and Taiwan Province) accounted for 25.9 percent of China’s total foreign trade. In those free trade agreements, basically 90 percent of imported products enjoy duty free treatment, and approximately 120 service sectors have been opened to foreign suppliers, compared to 100 service sectors in China’s commitments to the WTO at the time when China joined the organization. Committed to advancing economic globalization and safeguarding free trade, China is negotiating with relevant parties the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership for its early conclusion and implementation, and is accelerating the building of Free Trade Area of Asia-Pacific and East Asia Economic Community. With all these efforts, China will build a high standard network of free trade areas, focusing on the neighboring areas, radiating across the Belt and Road and open to the world.
Conclusion
The world is undergoing a new round of major development, great change and profound readjustment. The mankind still faces growing uncertainties and destabilizing factors. Surging tides of anti-globalization in recent years, coupled with rising protectionism and unilateralism, have posed severe challenges to the multilateral trading system with the WTO at its core.
Economic globalization has powered global growth and is an irreversible trend of our times. China and the multilateral trading system stand together through thick and thin. China will continue to fulfill its commitments, comply with rules, actively participate in the improvement of the multilateral trading system, and give firm support to the WTO in playing a greater role in global economic governance.
China’s economy has been transitioning from rapid growth to high-quality development. In this historic process, China will pursue with firmness the vision of innovative, coordinated, green, and open development that is for everyone, improve the socialist market economy system, and stimulate the vitality of various market entities.
China will take innovation as the primary driving force for development. China will adopt a more open attitude, strengthen the protection of innovation and intellectual property rights, and enhance international exchanges and cooperation. These efforts will ensure that technological development and innovation benefit not only China, but also the world, and its convenience readily accessible to more and more people.
China calls on all countries to jointly shoulder the responsibilities of our times and believes that all countries should have equal access to development opportunities. As the largest developing country in the world, China looks forward to further cooperation and communication with other countries to jointly respond to global issues that emerge in the process of globalization, and to building a global economic governance system based on equality, equity and win-win cooperation.
China commits itself to opening up wider and deeper to promote common development across the world, providing other countries with more opportunities to share the benefits of China’s development. China is willing to work hand-in-hand with its global trading partners to make economic globalization more open, inclusive, balanced and win-win with benefits to all so that different countries, different social strata and different groups of people all share in the benefits of economic globalization.
[1] China’s Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region, and Taiwan Province all became members of the WTO as separate customs territories at different times, the cases of which are not discussed in this white paper.


