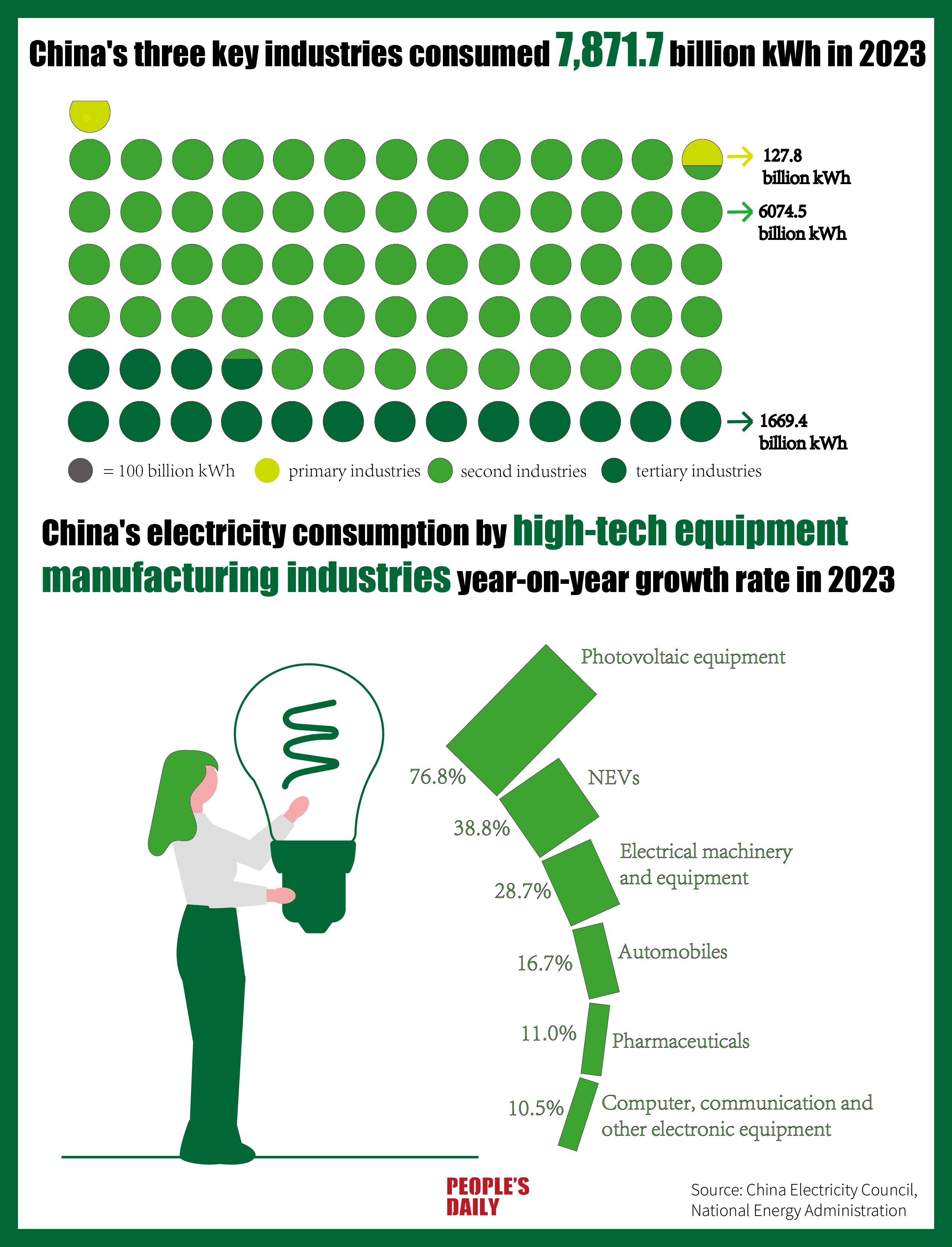
China's new quality productive forces are driving the growth of high-tech and innovative products, resulting in rapid electricity consumption growth in three key industries: primary (raw materials), secondary (finished goods), and tertiary (service sector). China's electricity consumption in these industries reached 7,871.7 billion kilowatt-hours (kWh) in 2023.
Amid China's high-tech and equipment manufacturing industry, the electricity consumption growth rate of industries like photovoltaic equipment manufacturing and new energy vehicle manufacturing is eye-catching.
Renewable energy became a new force to ensure the electricity supply in China's green energy transition.
From 2019 to 2022, China's electricity consumption, a key barometer of economic activity, maintained stable growth, while the amount of electricity generated from renewable energy compared to China's total electricity consumption grew from 28.2 percent to 31.6 percent.
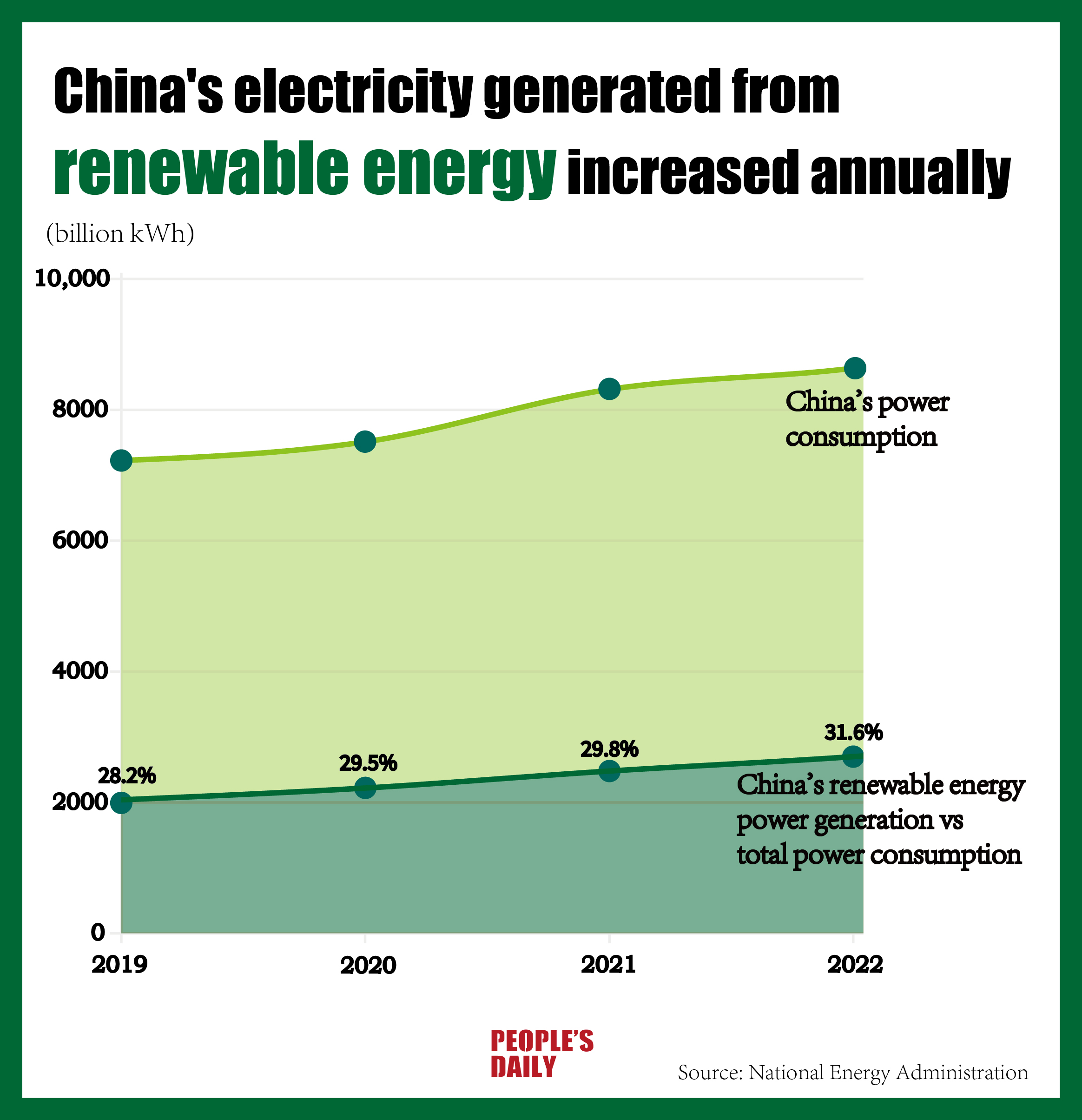
China's energy consumption has increased annually over the past five years as the proportion of clean energy, such as hydropower, nuclear power, and wind power, has increased.

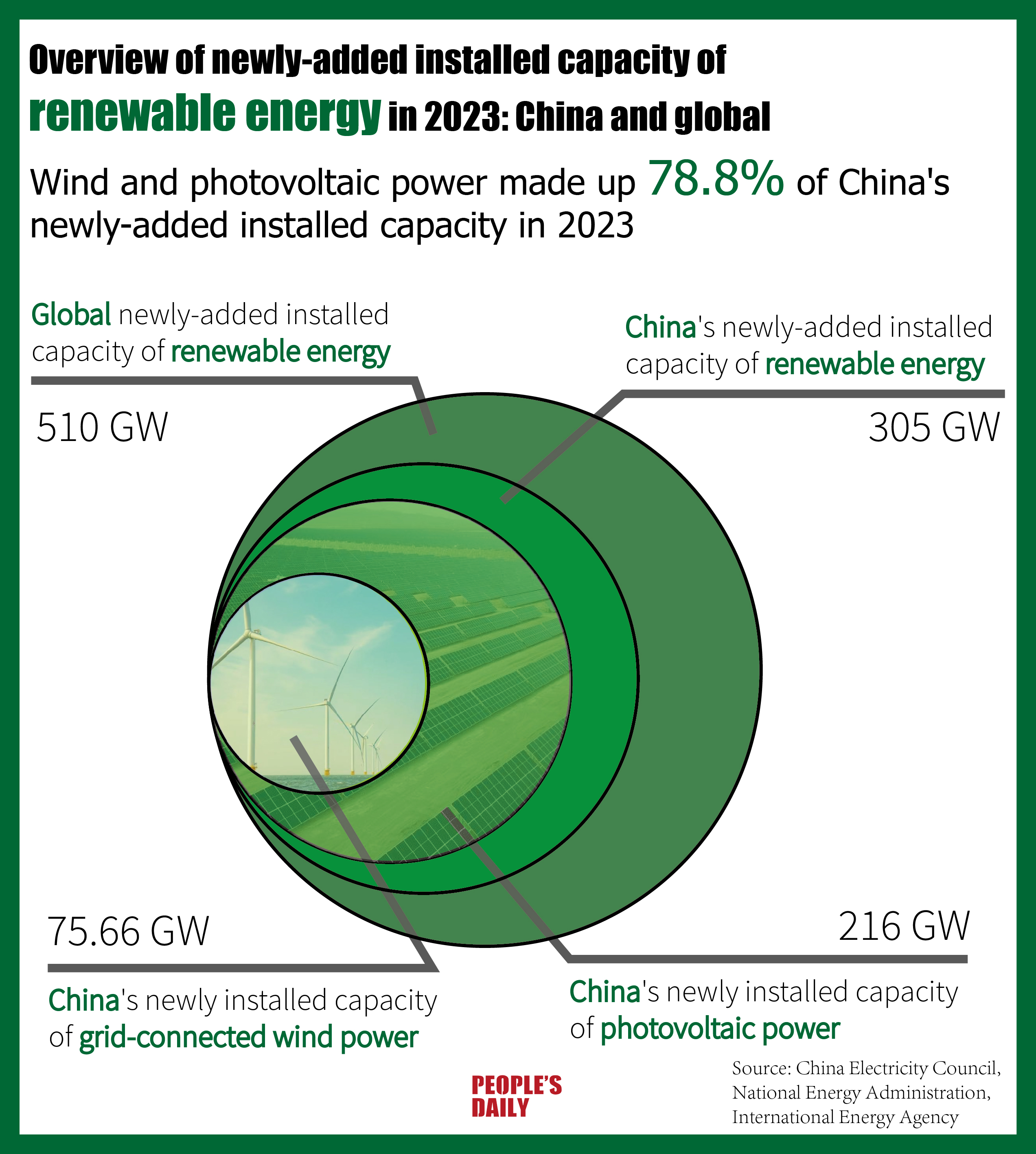
In 2023, China was the primary driving force behind the world's rapid renewable power generation capacity expansion, which grew by 50 percent to 510 gigawatts. It is worth mentioning that wind and photovoltaic power accounted for 78.8 percent of China's total newly added installed capacity in 2023.
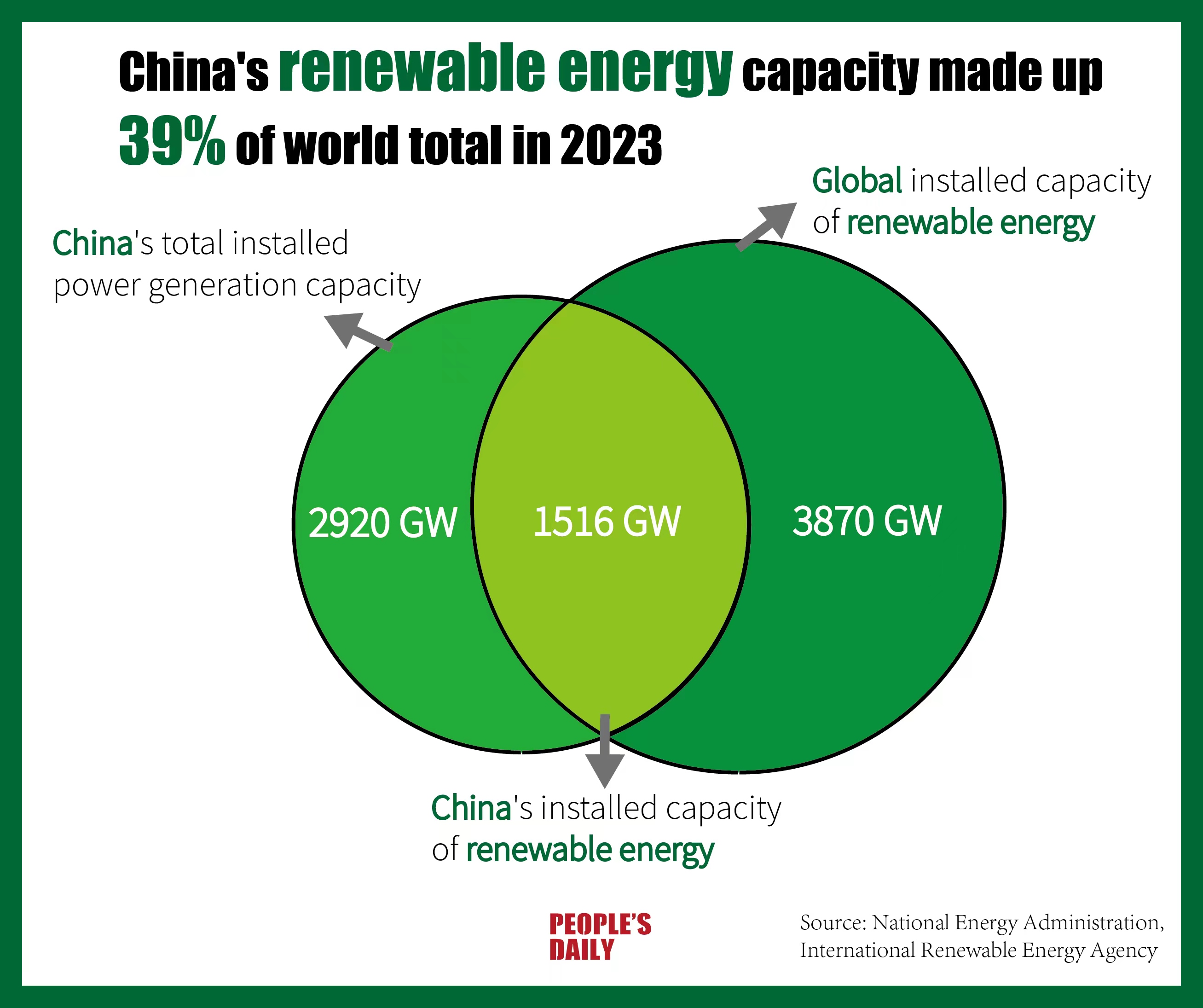
Meanwhile, China's installed renewable energy capacity exceeded 1,516 gigawatts in 2023, accounting for more than 50 percent of the country's total installed power generation capacity and 39 percent of global renewable energy capacity.
(Produced by Li Zhuoman, Liang Xiaojian; Edited by Han Xiaomeng)


