Illustration: Chen Xia/GT
Ten years ago, I went to New York City with the correspondent group of then Chinese premier Wen Jiabao's delegation. After we arrived, the Chinese side invited some former US senior officials and entrepreneurs to hold a symposium. At that time, the trade imbalance between China and the US was already prominent.
Wen gave the example of an iPod player, whose price was about $290 in the US at the time, but a Chinese manufacturer can only get $6 from each sale. I remember there was a heated discussion in China at that time - we would exchange 800 million shirts for a Boeing plane.
Do Americans earn more because they make more money? From what I have learned during my visits to the US these years, prices of commodities did not change much, or even become cheaper as production bases have been moved to China and other countries. But wages for middle- and low-income Americans have not risen much, or none at all. Reports show that in a 2015 contract between the United Automobile Workers and the Detroit automakers, senior workers received just a 2 percent annual pay increase, after suffering a 10-year pay freeze.
Where has Americans' income gone?
To answer this question, we need to look at the earnings of the biggest companies in the stock market. Apple, for example, was number one, with a net income of $57.4 billion in 2020, up from $14 billion in 2010. Of course, the growth of income of the senior executives at big companies and the big investors is even more startling. In January, The New York Times reported that "America's richest 10 percent, who own more than 80 percent of US stocks, have seen their wealth more than triple in 30 years, while the bottom 50 percent, relying on their day jobs in real markets to survive, had zero gains."
Economist Jonathan Rothwell listed an example in his book A Republic of Equals: A Manifesto for a Just Society: In Spain, Sweden and Iceland, doctors earn twice as much as the average worker, but in the US, physicians and surgeons earn nearly five times as much.
Such a huge gap between the rich and poor will bring at least two troubles for the future reforms in the US. First, the large-scale relief measures which aim at helping relieve the pressure of middle- and low-income Americans will actually help big enterprises, the rich and the upper class. In other words, the measures won't address the problem of the rich-poor gap.
Second, the US design of system is based on the principle of "profits first." But the increase of profits for big companies comes more and more at the cost of unemployment of the middle and lower classes. As New York Times columnist Thomas L. Friedman wrote, "We're in the middle of a pandemic that has crushed jobs and small businesses - but the stock market is soaring. That's not right. That's elephants flying. I always get worried watching elephants fly. It usually doesn't end well."
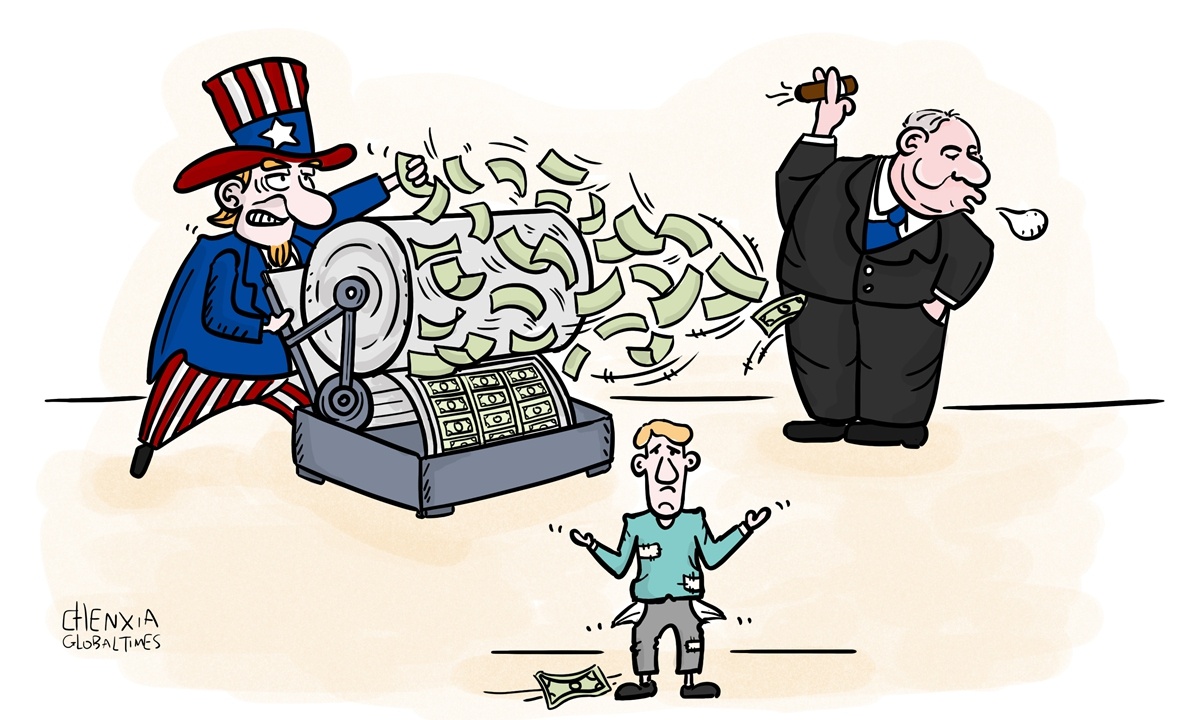
Both of these issues touch upon the old issue of raising taxes from big companies and from the rich. This will inevitably touch the foundation on which the US is built - competition in the free market economy which aims at improving efficiency. Moreover, getting vested interests to concede benefits is not an easy task.
If money can't be obtained from taxes, there is only one way to go: Printing more money. When things get to this point, it is no longer just a question of whether the social divisions can be healed, whether people can be united to move forward.
US economist Stephen Roach recently pointed out that last year, the combined COVID-19 relief packages in the US hit a total of $5 trillion, or 24 percent of GDP in 2020. This far exceeds all records. On March 6, US Senate passed President Joe Biden's $1.9 trillion COVID-19 relief bill.
Will this destroy the world's confidence in the dollar? After all, green note is the foundation of US hegemony.


