
Colorful writing is seen on the window of a reopened shop in Berlin, Germany, on May 9, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
The European Commission said in a recent economic forecast that despite a policy response at both the European Union (EU) and national levels, the EU economy will experience a historic recession this year due to the coronavirus pandemic.
Amid signs of stabilization recently, Europe is eager to resume work and production.
The gradual normalization of economic activities in Europe, together with economic recovery in China, will contribute effectively as the stabilizer for the world economy, analysts say.
HISTORIC RECESSION
The European Commission projects that the euro-area economy and the EU economy will contract by a record 7.75 percent and 7.5 percent, respectively, in 2020.
"Europe is experiencing an economic shock without precedent since the Great Depression," European Commissioner for the Economy Paolo Gentiloni has said.
The risks surrounding the forecasts are also exceptionally large and concentrated on the downside, as it's not certain when the pandemic will end, said the EU's executive arm.
For the European economic engine, the gross domestic product (GDP) in Germany was down seasonal and calendar adjusted by 2.2 percent in the first quarter of 2020 compared to the previous quarter, the Federal Statistical Office (Destatis) said Friday.
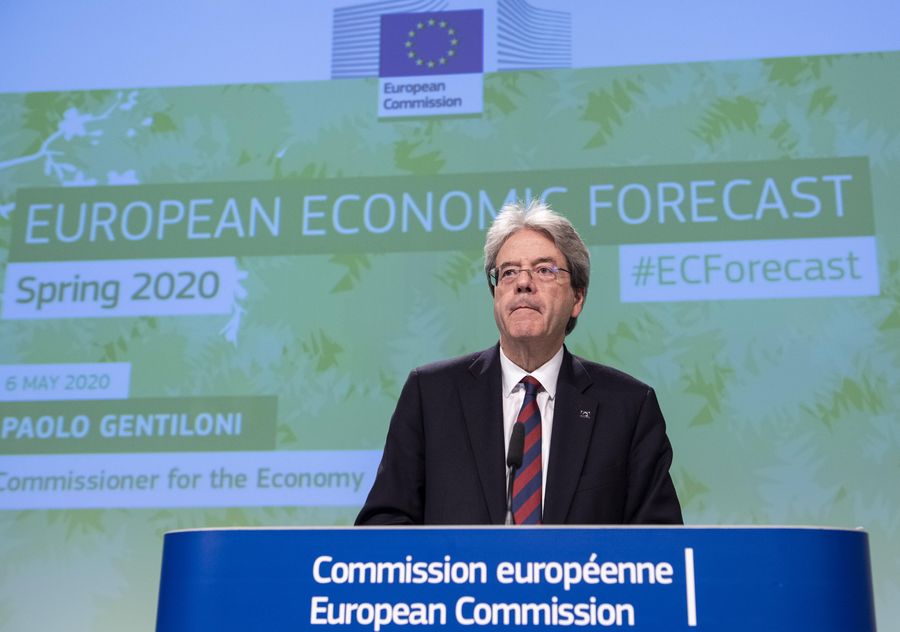

Paolo Gentiloni, European Commissioner for the Economy, attends a press conference in Brussels, Belgium, May 6, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
The German government is bracing for the "worst recession" in the country's history, with its GDP expected to fall by 6.3 percent this year, Minister for Economic Affairs and Energy Peter Altmaier announced at the end of April.
In April, France's national statistics institute INSEE said its GDP tumbled by 5.8 percent in the first quarter, its deepest drop on the quarterly basis since World War II. And the government forecast a contraction of 8 percent for the whole year. The central bank BdF estimated that every two-week containment would lead to a 1.5-percent loss in the GDP.
Britain's GDP fell by 2 percent quarter on quarter in the first three months of 2020, the largest quarterly fall since the financial crisis in late 2008, the Office for National Statistics said.
"Technically a recession is defined as two quarters of negative GDP, we've now had one ... so yes, it is now very likely that the UK is facing a significant recession at the moment and this year," British Chancellor of the Exchequer Rishi Sunak said recently.
The situation in Italy is even worse. Italy's GDP contracted by 4.8 percent in the first quarter, Italy's National Statistics Institute said on April 30.
VARIOUS STIMULUS MEASURES
In order to boost its pandemic response, from the European level to the national level, all major economies are rolling out various stimulus measures and making their best efforts.
President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Christine Lagarde speaks at an online event organized by the Italy-based European University Institute. (Photo: Xinhua)
The European Central Bank (ECB) has recently decided to leave key interest rates for the euro area unchanged while introducing a series of new measures.
The ECB Governing Council said the eurozone base interest rate will remain at 0.00 percent, with the marginal lending rate and deposit rate remaining at 0.25 percent and minus 0.50 percent, respectively.
On the national level, Germany's Ministry of Finance announced on May 14 that the German government had adopted a range of measures to help companies and employees during the coronavirus crisis, for example by increasing financial support in short-time work or by providing loans for companies and businesses.
According to the German government, 1 million applications for immediate financial aid for small companies and self-employed people had been approved in less than four weeks.
The approved state aid amounted to around 8 billion euros (8.7 billion dollars), according to the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. Self-employed and small companies with up to 10 employees can apply for emergency funds of up to 15,000 euros (16,232 dollars) from the German government. The one-off funds do not have to be repaid.

A man walks past posters encouraging people to have faith during the coronavirus outbreak in London, Britain on April 30, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
From May 11 onwards, France entered a partial and gradual deconfinement after eight weeks of strict quarantine to stem the coronavirus epidemic. Some 400,000 non-food businesses reopened in France, which represented 900,000 jobs.
To mitigate the pandemic's economic fallout, the French government has mobilized over 110 billion euros (119 billion dollars) to help companies stay afloat, consisting, in large part, of partial unemployment scheme, state loan guarantees and tax and payroll charge deferrals.
In Britain, the government unveiled a vast economic backstop in late March, telling British businesses of all size that it would cover 80 percent of the pay of workers who are temporarily laid-off for up to 2,500 pounds (2,903 dollars) a month each, in order to prevent wide-scale layoffs resulted from the coronavirus pandemic.
During the week, Italian Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte's cabinet passed a decree containing financial measures worth 55 billion euros (59.6 billion dollars) to support the economy hard hit by the coronavirus pandemic.

A worker disinfects a hair salon which is about to resume operation in Rome, Italy, May 14, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
ECONOMIC STABILIZER
Looking upon all the measures, resumption in European countries is officially on the agenda. European workers are getting back to work, and many factories are resuming their production.
Meanwhile, major progress has been made in the prevention and control of the epidemic in China, with the resumption of production reaching a high level.
This situation is of great value not only for the restoration of economic order in China and Europe, but also for the gradual recovery of industrial and supply chains between China and Europe, said Tang Zheng, vice president of the European Working Committee of CEATEC, a non-governmental body for technical and economic cooperation between China and Europe.

Vehicles are seen at a car dealership of Volkswagen in Berlin, capital of Germany, May 7, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
"In the long run, it will help the continuation of the globalization process," he said. Meanwhile, he added, as one of China's major trading partners, EU recovery will undoubtedly play a positive role in bringing China's economy on track.
In addition to expanding economic cooperation and supplying anti-epidemic materials, Tang believed that China may also be able to share its experience in production resumption and help Europe reduce the risk of a second wave of infection.
Tang's opinion is also shared by Mao Xuxin, an economist at London-based think-tank the National Institute of Economic and Social Research.

A general view of the Bank of England in London, Britain. (Photo: Xinhua)
According to Mao, with the resumption of work and production of enterprises, China's economy has shown a strong sign of recovery from the end of the first quarter. As the EU's biggest source of imports and its second-biggest export market, China plays an important role in Europe's economic recovery from the pandemic shock.
"In many other parts of the world, the COVID-19 pandemic is not reaching its peak and continues to cause health care and economic catastrophe. With economic recovery from both China and Europe, the world economies will approach stabilization by the end of this year and grow again in 2021," Mao told Xinhua.
"As the only major economy with the purchasing managers' index above 50 in March and April, China's economic growth is an effective stabilizer for the world economy to avoid a deep recession this year," he added.

Schoolchildren wearing face masks keep social distancing as they enter the reopened Simone Veil Primary School in Nice, France, May 12, 2020. (Photo: Xinhua)
Pierre Picquart, a French specialist in geopolitics and professor at University of Paris-VIII, told Xinhua that China has already started its economic recovery. While many countries are in containment, the Chinese economy stabilized at the end of the first quarter of 2020.
The growth started again in China in the second quarter of 2020 and economic activity finds the path of expansion, he said, adding that "the success of China's economic recovery is great news for all nations."
This means that "priority No. 1" is to restore confidence by revitalizing the Chinese and global economy, Picquart said, adding China's economic recovery will revive the world economy.


